Unveiling the mysteries of life’s evolution, the Evidence for Evolution Webquest Answer Key PDF stands as an authoritative guide, meticulously crafted to illuminate the compelling evidence supporting the theory of evolution. Delve into the fascinating realm of comparative anatomy, where homologous and analogous structures whisper tales of common ancestry.
Explore the captivating world of fossils, where transitional forms bridge the gaps between species. Discover the power of molecular evidence, as DNA and protein sequences unravel the genetic tapestry of life’s diversity.
Journey through the realms of biogeography, where the distribution of species across the globe paints a vivid picture of evolutionary processes. Witness the remarkable insights offered by embryology, as the development of embryos reveals profound connections between different species. And finally, grasp the fundamental principles of natural selection, the driving force behind the adaptation and diversification of life on Earth.
Evidence for Evolution: Evidence For Evolution Webquest Answer Key Pdf
The theory of evolution, proposed by Charles Darwin in the 19th century, is a widely accepted scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. Over the years, extensive evidence has been gathered to support the theory, solidifying its position as a fundamental principle in biology.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy examines the similarities and differences in the anatomical structures of different organisms. By comparing homologous structures (structures that share a common evolutionary origin) and analogous structures (structures that perform similar functions but do not share a common origin), scientists can infer evolutionary relationships.
- Homologous structures, such as the forelimbs of humans and bats, provide evidence for common ancestry, despite their different functions.
- Analogous structures, such as the wings of bats and birds, demonstrate convergent evolution, where different organisms independently evolve similar traits to adapt to similar environments.
Fossils
Fossils are preserved remains or traces of organisms from the past. They provide a direct record of past life and allow scientists to study the evolution of species over time.
- Process of fossilization:Fossils form when organisms are buried and gradually replaced by minerals.
- Types of fossils:Fossils include body fossils (preserved remains of organisms), trace fossils (evidence of an organism’s activity), and chemical fossils (preserved molecules or compounds).
- Transitional fossils:Transitional fossils exhibit characteristics of both ancestral and descendant species, providing evidence for gradual evolutionary change. For example, Tiktaalik roseae is a transitional fossil between fish and amphibians.
Molecular Evidence
Molecular evidence, such as DNA and protein sequences, provides valuable insights into evolutionary relationships.
- Genetic similarities:Closely related species share a higher percentage of genetic similarity than distantly related species.
- Molecular clocks:Mutations accumulate at a relatively constant rate over time, allowing scientists to estimate the time since two species diverged.
- Phylogenetic trees:Phylogenetic trees are diagrams that represent evolutionary relationships based on molecular data, showing how different species are related to each other.
Biogeography
Biogeography examines the distribution of species around the world. It provides evidence for evolution by demonstrating how species have adapted to different environments and how geographic barriers have influenced their evolution.
- Continental drift:The movement of continents over time has played a significant role in the evolution of species by separating populations and allowing them to evolve independently.
- Endemic species:Endemic species are found only in specific geographic regions, indicating that they have evolved in isolation from other populations.
- Adaptive radiation:Adaptive radiation occurs when a group of species rapidly diversifies into a variety of ecological niches, often in response to changes in the environment.
Embryology
Embryology studies the development of embryos. By comparing the embryonic development of different species, scientists can gain insights into their evolutionary relationships.
- Similarities in early development:Embryos of different species often exhibit striking similarities in their early stages, suggesting a shared ancestry.
- Vestigial structures:Vestigial structures are remnants of organs or structures that were functional in ancestral species but have become reduced or lost in descendant species. They provide evidence for evolutionary change.
- Haeckel’s law:Haeckel’s law states that “ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny,” meaning that the development of an individual organism (ontogeny) mirrors the evolutionary history of its species (phylogeny).
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the driving force behind evolution. It occurs when individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing.
- Variation:Individuals within a population exhibit variation in their traits.
- Heritability:Traits can be passed on from parents to offspring.
- Selection:Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their traits to the next generation.
- Adaptation:Over time, natural selection leads to the accumulation of favorable traits in a population, resulting in adaptations that enhance the species’ survival and reproductive success.
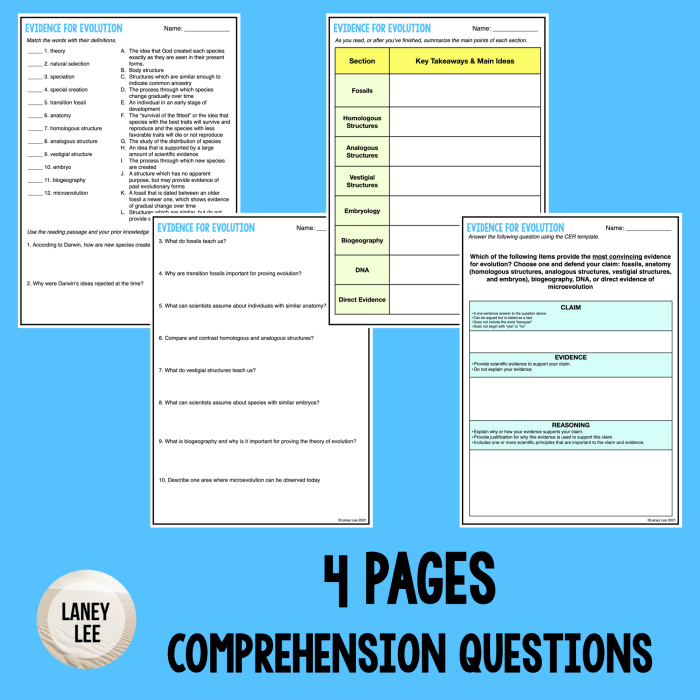
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of homologous structures in comparative anatomy?
Homologous structures provide compelling evidence for common ancestry, as they share a similar underlying structure and developmental origin despite serving different functions in different species.
How do transitional fossils contribute to our understanding of evolution?
Transitional fossils represent intermediate forms between ancestral and descendant species, bridging the gaps in the fossil record and providing direct evidence for gradual evolutionary change.
What role does molecular evidence play in supporting the theory of evolution?
Molecular evidence, such as DNA and protein sequences, allows scientists to compare the genetic makeup of different species, revealing similarities and differences that shed light on evolutionary relationships.


