Type b- agglutinates in anti-b and anti-rh sera. – Type B agglutinates in anti-B and anti-Rh sera is a topic of great importance in blood typing and transfusion medicine. This article delves into the structure, reactivity, and clinical implications of type B agglutinogens, exploring their presence in anti-Rh sera and the potential for cross-reactivity between anti-B and anti-Rh antibodies.
Understanding the behavior of type B agglutinates in these sera is crucial for accurate blood typing and safe transfusion practices, ensuring patient safety and optimal healthcare outcomes.
Type B Agglutinogens and Anti-B Sera
Type B agglutinogens are antigens present on the surface of red blood cells in individuals with type B blood. They are composed of complex carbohydrates attached to a protein backbone. Anti-B sera contain antibodies that specifically recognize and bind to type B agglutinogens, causing agglutination (clumping) of red blood cells.
Specificity and Reactivity of Anti-B Sera
- Anti-B sera only react with type B agglutinogens.
- They do not react with type A or O agglutinogens.
- The strength of agglutination depends on the concentration of anti-B antibodies in the serum and the number of type B agglutinogens on the red blood cells.
Type B Agglutinogens in Anti-Rh Sera
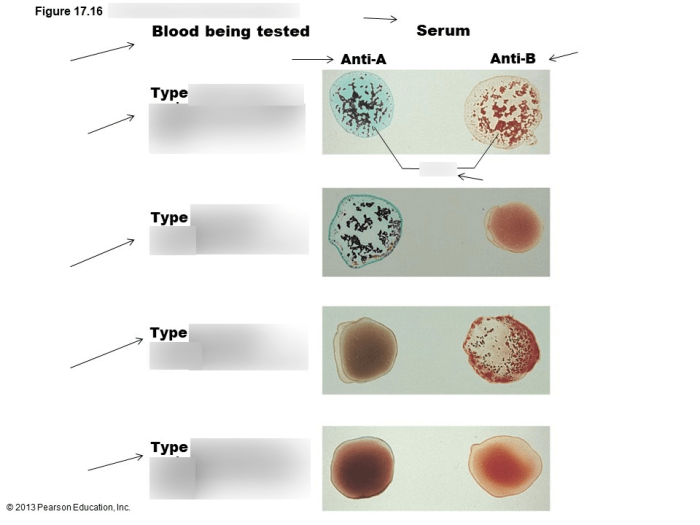
In some cases, type B agglutinogens may be present in anti-Rh sera. This is due to the presence of antibodies that cross-react with both type B agglutinogens and Rh antigens.
Cross-Reactivity between Anti-B and Anti-Rh Antibodies
- Cross-reactivity occurs when antibodies bind to antigens that are similar but not identical to the target antigen.
- In the case of type B agglutinogens and Rh antigens, the antibodies in anti-Rh sera may recognize certain structural similarities between the two antigens.
- This cross-reactivity can lead to agglutination of red blood cells that have type B agglutinogens in anti-Rh sera.
Clinical Significance
Type B agglutination in anti-B and anti-Rh sera has important clinical implications in blood typing and transfusion medicine.
Blood Typing
- Type B agglutination in anti-B sera is used to determine the ABO blood group of an individual.
- If agglutination occurs, the individual has type B blood.
- If no agglutination occurs, the individual has type A, O, or AB blood.
Transfusion Medicine, Type b- agglutinates in anti-b and anti-rh sera.
- Type B agglutination in anti-Rh sera can lead to false-positive results in Rh typing.
- This can result in incorrect blood transfusions, which can be life-threatening.
- Therefore, it is important to use specific anti-Rh sera that do not cross-react with type B agglutinogens.
Case Studies: Type B- Agglutinates In Anti-b And Anti-rh Sera.
There have been several reported cases of type B agglutination in anti-B and anti-Rh sera.
Case Study 1
- A patient with type B blood received a transfusion of blood that was incorrectly typed as type O.
- The patient’s red blood cells agglutinated in anti-Rh sera, leading to a false-positive Rh typing.
- The patient received an incorrect blood transfusion, which resulted in a transfusion reaction.
Research Directions

Ongoing research is focused on developing new methods to detect and prevent type B agglutination in anti-B and anti-Rh sera.
Potential Future Applications
- Improved blood typing methods to prevent false-positive results.
- Development of specific anti-Rh sera that do not cross-react with type B agglutinogens.
- New strategies to prevent transfusion reactions caused by type B agglutination.
FAQ Summary
What are type B agglutinogens?
Type B agglutinogens are glycoproteins present on the surface of red blood cells that are recognized by anti-B antibodies.
What is the significance of type B agglutinates in anti-Rh sera?
The presence of type B agglutinates in anti-Rh sera can lead to false-positive reactions in Rh typing, potentially resulting in incorrect blood transfusions.
How can cross-reactivity between anti-B and anti-Rh antibodies be managed?
Cross-reactivity can be managed through careful antibody screening and testing, as well as the use of specific reagents to differentiate between anti-B and anti-Rh antibodies.