The time between failures for an electrical appliance – The time between failures (TBF) for electrical appliances is a critical metric that measures the reliability and durability of these devices. Understanding TBF is essential for manufacturers, consumers, and service providers alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of TBF, exploring its importance, influencing factors, estimation methods, applications, and strategies for improvement.
The TBF for an electrical appliance represents the average period of time between its failures. It is a key indicator of the appliance’s quality, performance, and expected lifespan. A high TBF signifies a reliable and durable appliance, while a low TBF suggests potential issues with design, manufacturing, or usage.
1. Introduction: The Time Between Failures For An Electrical Appliance
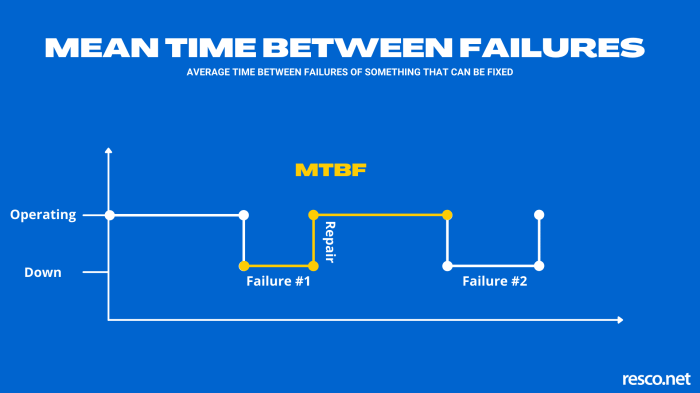
Time between failures (TBF) is a crucial metric used to assess the reliability and durability of electrical appliances. It represents the average period of operation before a failure occurs, providing insights into the appliance’s performance and lifespan.
2. Factors Affecting TBF
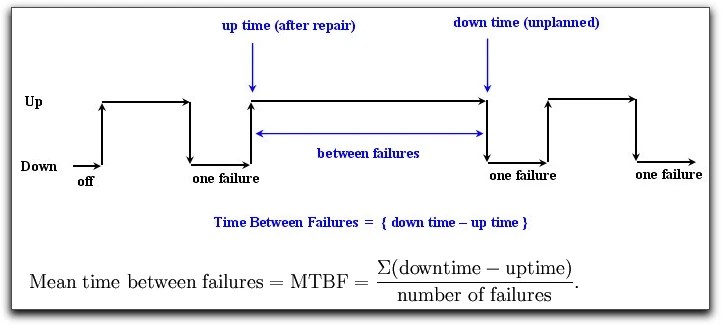
TBF is influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Design and manufacturing quality: Robust designs, high-quality materials, and precise assembly practices contribute to longer TBF.
- Operating conditions: Temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors can impact component performance and TBF.
- Usage patterns: Heavy or continuous use can shorten TBF, while intermittent use may extend it.
- Maintenance and repair practices: Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and proper handling can significantly improve TBF.
3. Methods for Estimating TBF
TBF can be estimated using various methods:
- Historical data analysis: Analyzing past failure records provides insights into TBF and helps identify patterns.
- Reliability testing: Conducting controlled experiments under specific conditions to assess component or system reliability and estimate TBF.
- Simulation modeling: Using computer models to simulate appliance operation and predict TBF under different scenarios.
4. Applications of TBF
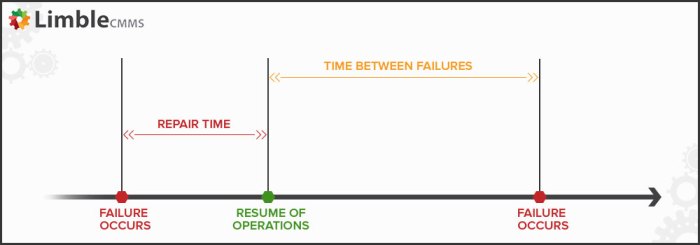
TBF has practical applications in:
- Product design and development: Optimizing designs and selecting reliable components to enhance TBF.
- Warranty and service planning: Establishing appropriate warranty periods and service intervals based on TBF estimates.
- Predictive maintenance strategies: Monitoring appliance performance and predicting potential failures to schedule proactive maintenance.
5. Improving TBF
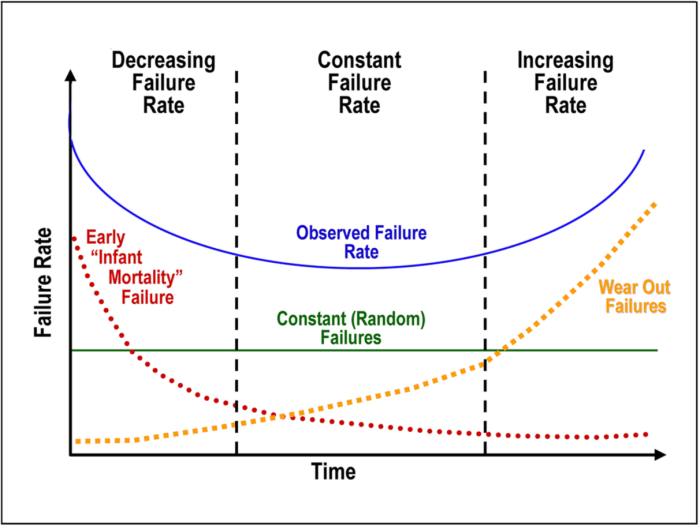
Improving TBF requires:
- Design optimization: Incorporating design features that enhance component reliability and reduce failure risk.
- Quality control measures: Implementing rigorous quality control processes during manufacturing to minimize defects and ensure component integrity.
- Proper operating practices: Educating users on proper appliance usage, handling, and maintenance practices to prolong TBF.
- Regular maintenance and repairs: Performing scheduled maintenance, inspections, and repairs to identify and address potential issues early on.
FAQ Insights
What is the time between failures (TBF)?
TBF is the average period of time between failures for an electrical appliance.
Why is TBF important?
TBF is important because it indicates the reliability and durability of an electrical appliance, which influences purchasing decisions, warranty planning, and maintenance strategies.
What factors affect TBF?
TBF can be influenced by factors such as design and manufacturing quality, operating conditions, usage patterns, and maintenance practices.
How can TBF be estimated?
TBF can be estimated using historical data analysis, reliability testing, or simulation modeling.
How can TBF be improved?
TBF can be improved through design optimization, quality control measures, proper operating practices, and regular maintenance and repairs.